Author: Megan Jones (Adv.Dip.NutMed, BHsc.NutMed)
When we get sick the cells of our immune system take a big hit1. As a result, we become tired and lethargic and, as we all know, if we don’t rest, we stay sick for longer.[2]
Whilst sleep is an important factor in recovery from illness, optimising our nutrition is fundamental[3] in supporting our immune response right down at a cellular level.[4]
Here, we take a deep dive into the relationship between energy and immunity, how a nutritionally replete diet can support a robust immune system and overall energy and vitality, and how supplements like Nuzest’s Good Green Vitality can help ensure your body is getting all the nutrients it needs for a healthy immune system.
Key takeaways:
- Our immune systems require support in the form of nutrients in order to function optimally.[7]
- When our nutrition is lacking, our energy levels can start to diminish.[11]
- The body’s entire immune response can be altered by one single nutrient deficiency.[13]
- Optimising our nutrition with whole foods and highly bioavailable nutritional supplementation can support both our immunity and our body’s natural energy production.[15],[16]
Why do our immune systems need nutrition?
If you haven’t had a cough or sniffle recently, the chances are you will know someone who has! Research tells us that adults will experience up to four common colds each year, with a huge one billion colds experienced each year in the US alone.[5]
While a strong immune system helps ward off colds and flus, it also targets bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi as well, and works to remove them from our body.[6]
Just like our car needs fuel to drive, or we need that smoothie in the morning to get going, our immune system is highly dependent on the availability of nutrients[7].These nutrients include vitamins, minerals, micronutrients, macronutrients, and antioxidants; all playing an important role in supporting the growth and function of immune cells and promoting the production of antibodies.[8]
We have known for a long time that nutrition is intricately linked to immunity.[12] In fact, nutrition is a critical factor when it comes to our overall health and well-being[9], with research telling us that a well-functioning immune system is essential for our survival.[10]
However, even if our immune system is fuelled, robust and thriving, it can only fight off bugs for so long. So, if we are not consistently consuming adequate nutrition, our immunity can start to weaken. When our immune system is depleted, we find our energy levels start to diminish as well.[11]
How can we support energy production?
What is surprising to many is that a deficiency of any single nutrient has the potential to alter the body's entire immune response.[13]
Furthermore, our immune system can become dysfunctional even when our bodies don’t get enough energy from the food we eat. Along with nutritional deficiencies, this lack of energy can weaken the immune system to the point of becoming more susceptible to diseases and infections.[14]
A balanced diet with optimal energy intake supports the immune system's functioning and enhances its ability to fight off these infections and disease-causing pathogens.[15]
To achieve optimal energy production and provide this energy to our bodies at a cellular level, the food we consume breaks down into various nutrients, including carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and is then utilised as energy. The energy produced is used for various biological system functions within the body, including the important role of maintaining of our immune system.[16]
How do nutrients support our immunity?
Nutritional deficiencies are closely associated with impaired immune response and susceptibility to infection.6 In order to mitigate this, focussing on consumption of immune-modulating nutrients by way of whole foods and/or high-quality nutritional supplementation is key in supporting our immunity.
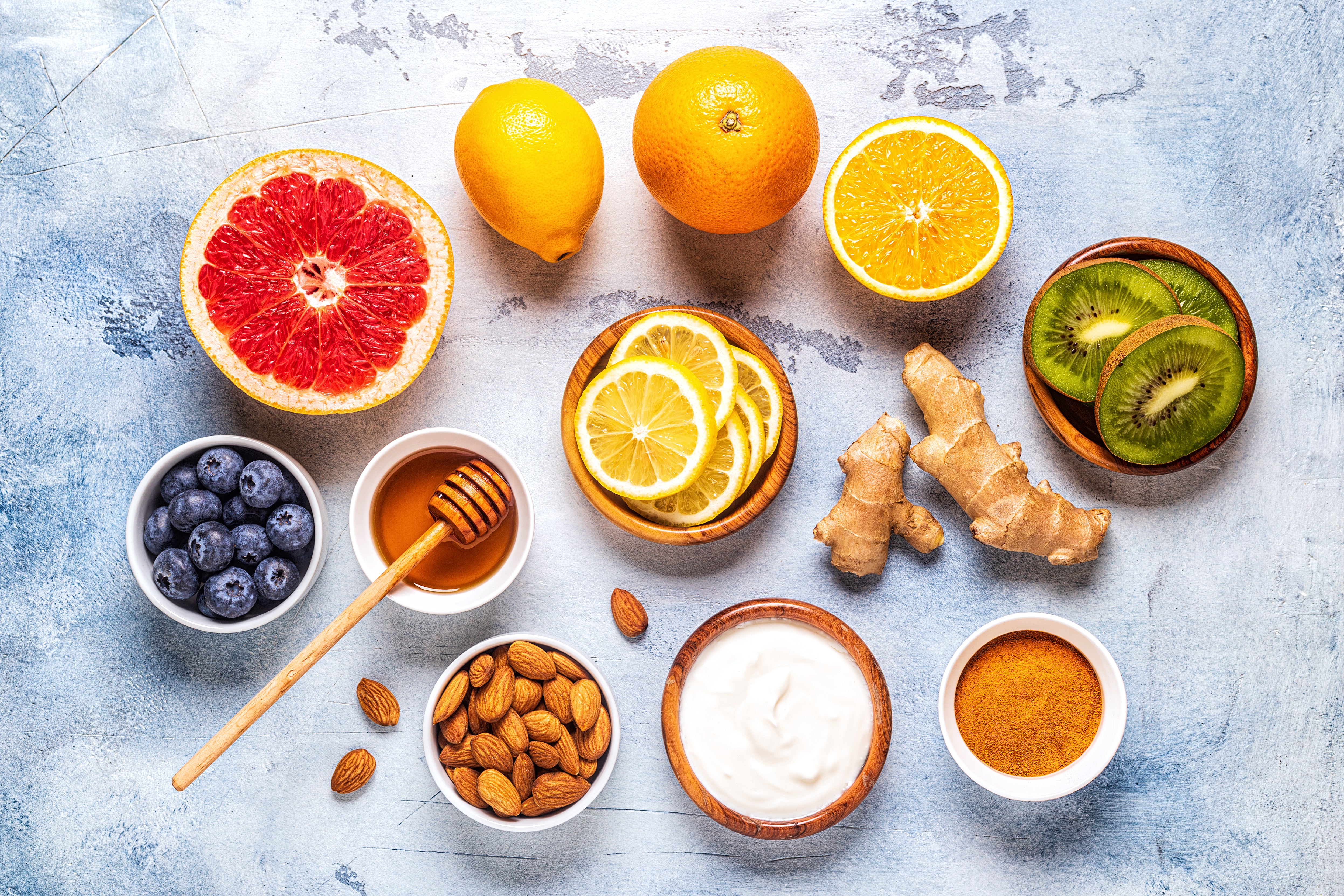
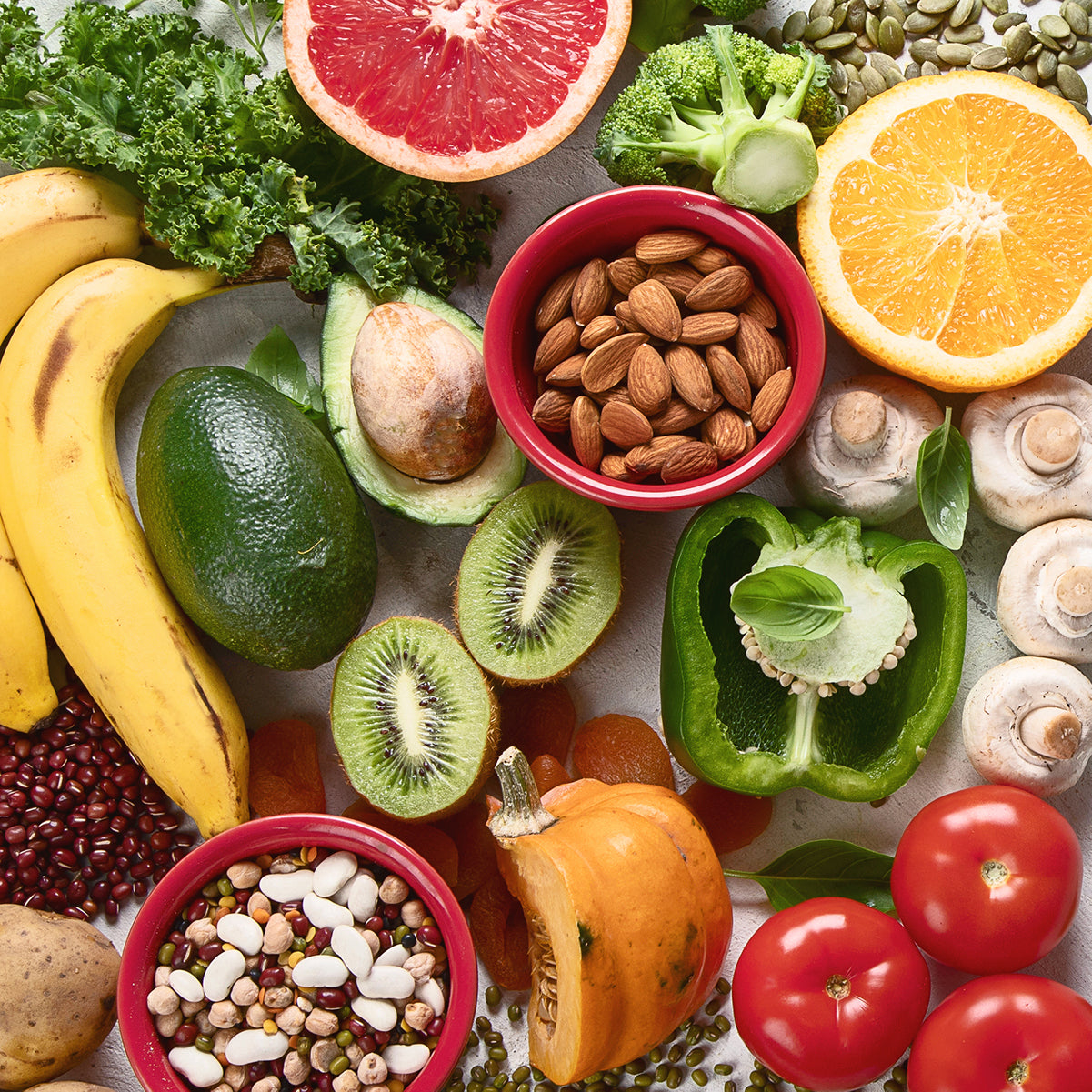
Bearing in mind that we need to consume an adequate amount of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, let’s have a look at five key nutrients to support your energy and immunity.
Top 5 nutrients to support our energy and immunity:
1. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system's functioning. It helps in the production of white blood cells, which fight off infections and diseases.
We see high vitamin C levels in citrus fruits, as well as capsicum, kiwi fruit, tomatoes, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower.
2. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that supports the immune system's functioning. Just like vitamin C, it helps in the production of white blood cells and antibodies, which fight off infections and diseases. Even a mild deficiency in zinc has been associated with widespread defects in both the adaptive and innate immune responses.[9]
Foods that are high in zinc include oysters, chicken, legumes, nuts/seeds, crab, lobster and red meat.
3. B vitamins
A diet rich in B-group vitamins is essential for optimal body and brain function by way of cellular energy and metabolism, and insufficient amounts of such vitamins have been associated with higher levels of inflammation and manifestations of fatigue.[17],[18]
You’ll find B vitamins in foods such as peas, nuts, leafy greens, wholegrains and liver.
4. Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for a healthy immune system. They help in the production of anti-inflammatory compounds to reduce inflammation and support proper function of our immune system.[19]
Foods that are high in Omega-3 fatty acids include cold-water fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring and sardines, as well as nuts and seeds like chia, walnuts, flaxseeds and oils such as cod liver oil, flaxseed, fish and krill oil.
5. Probiotics
While probiotics support the natural balance of the gut microbiome, they also provide protection against disease-causing bacteria by targeting the unwanted bacteria in the gut. This in turn can modulate and support our body’s immune system.20
A general guideline for incorporating probiotics into your diet is to just add as many fermented foods as possible. These include foods such as yoghurt, kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, pickles, miso, tempeh, kimchi and sourdough bread.
How can we ensure we are getting the Top 5 in our diet?
Here at Nuzest, we firmly believe that food comes first. Nothing can replace a healthy, varied diet, but we also know that it’s not always realistic to get all the nutrients we need to thrive through our diets alone. This is why we developed Good Green Vitality – a comprehensive multi-nutrient formula to help fill any nutritional gaps in your diet.
We carefully selected the specific forms of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients in Good Green Vitality based on science and research, with efficacy being the driving force behind our formulation. This means that the body’s absorption process is not hindered by cheaper forms of ingredients, and it is able to transport all nutrients efficiently and directly to the blood, in order to support the body’s natural energy and immunity.
If you are looking to support your immune system and your energy with our Top 5 nutrients, then look no further than Good Green Vitality; a delicious everyday multi-nutrient supplement that can be mixed either in water or your morning smoothie.
References:
- Nicholson L. B. (2016). The immune system. Essays in biochemistry, 60(3), 275–301. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20160017
- Watson S, Cherney K. 11 Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body [Internet]. Healthline. 2020. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/health/sleep-deprivation/effects-on-body
- Moisey, L. L., Merriweather, J. L., & Drover, J. W. (2022). The role of nutrition rehabilitation in the recovery of survivors of critical illness: underrecognized and underappreciated. Critical care (London, England), 26(1), 270. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-022-04143-5
- Karagiannis, S. N., & Arnold, J. N. (2022). Immune cell-antibody interactions in health and disease. Clinical and experimental immunology, 209(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/cei/uxac065
- WebMD. WebMD; 2022. Available from: https://www.webmd.com/cold-and-flu/common_cold_overview
- InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. How does the immune system work? [Updated 2020 Apr 23]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279364/
- Gombart, A. F., Pierre, A., & Maggini, S. (2020). A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients, 12(1), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010236
- Noor, S., Piscopo, S., & Gasmi, A. (2021). Nutrients Interaction with the Immune System. Archives of Razi Institute, 76(6), 1579–1588. https://doi.org/10.22092/ari.2021.356098.1775
- Childs, C. E., Calder, P. C., & Miles, E. A. (2019). Diet and Immune Function. Nutrients, 11(8), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081933
- Simon, A. K., Hollander, G. A., & McMichael, A. (2015). Evolution of the immune system in humans from infancy to old age. Proceedings. Biological sciences, 282(1821), 20143085. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.3085
- Dantzer, R., Heijnen, C. J., Kavelaars, A., Laye, S., & Capuron, L. (2014). The neuroimmune basis of fatigue. Trends in neurosciences, 37(1), 39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2013.10.003
- Ask the Expert: The role of diet and nutritional supplements during COVID-19 [Internet]. The Nutrition Source. 2020. Available from: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2020/04/01/ask-the-expert-the-role-of-diet-and-nutritional-supplements-during-covid-19/
- Boston 677 HA, Ma 02115 +1495-1000. Nutrition and Immunity [Internet]. The Nutrition Source. 2020. Available from: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/nutrition-and-immunity/#:~:text=A%20deficiency%20of%20single%20nutrients
- Smith, T. J., & McClung, J. P. (2021). Nutrition, Immune Function, and Infectious Disease. Medical journal (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.), (PB 8-21-01/02/03), 133–136.
- Calder, P. C., Carr, A. C., Gombart, A. F., & Eggersdorfer, M. (2020). Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections. Nutrients, 12(4), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041181
- Morris AL, Mohiuddin SS. Biochemistry, Nutrients. [Updated 2022 May 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554545/
- Ford, T. C., Downey, L. A., Simpson, T., McPhee, G., Oliver, C., & Stough, C. (2018). The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial. Nutrients, 10(12), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121860
- Tardy, A. L., Pouteau, E., Marquez, D., Yilmaz, C., & Scholey, A. (2020). Vitamins and Minerals for Energy, Fatigue and Cognition: A Narrative Review of the Biochemical and Clinical Evidence. Nutrients, 12(1), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010228
- Gutiérrez, S., Svahn, S. L., & Johansson, M. E. (2019). Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(20), 5028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205028
- Yan, F., & Polk, D. B. (2011). Probiotics and immune health. Current opinion in gastroenterology, 27(6), 496–501. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834baa4d